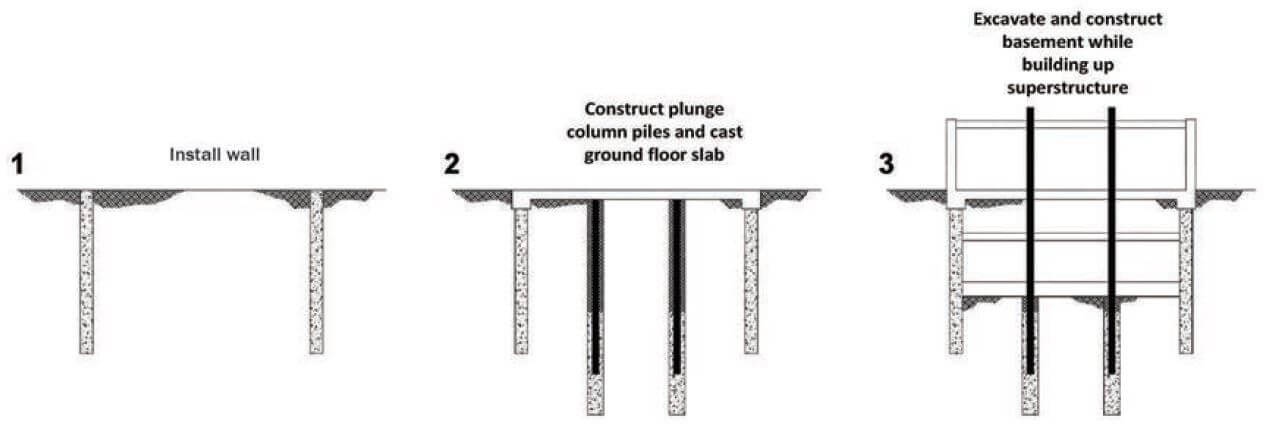
This element is unique in that it contains both vertical rising walls and horizontal elements ground floor slabs and comprises work from a number of separate work sections and trades e g.
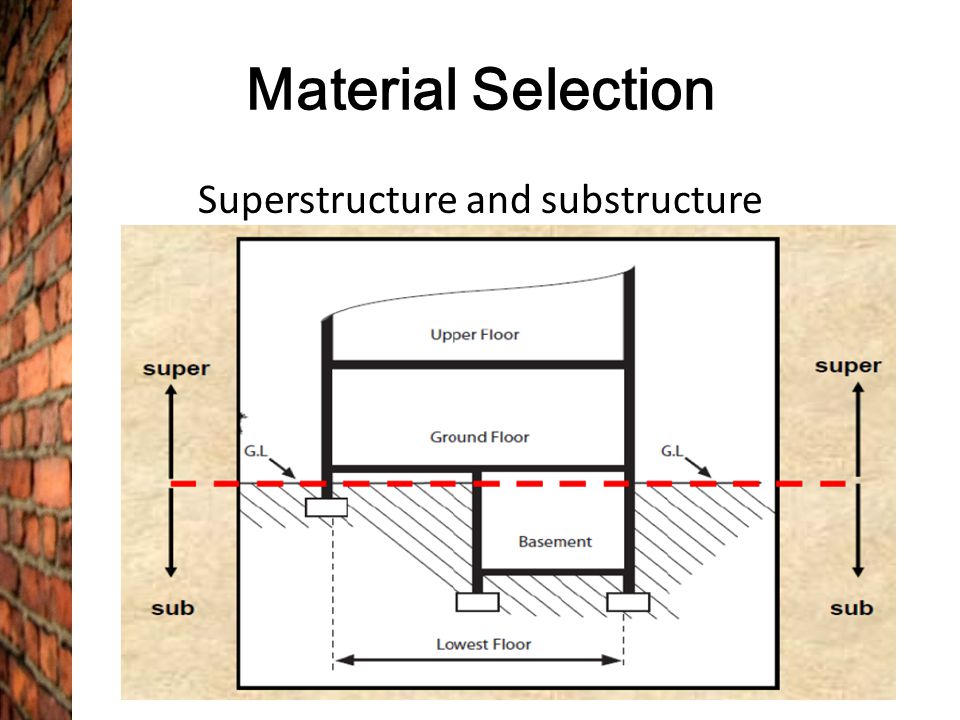
Ground floor slab substructure or superstructure.
B4 6 superstructure principal load bearing elements.
5 substructure ground floors drainage and basements.
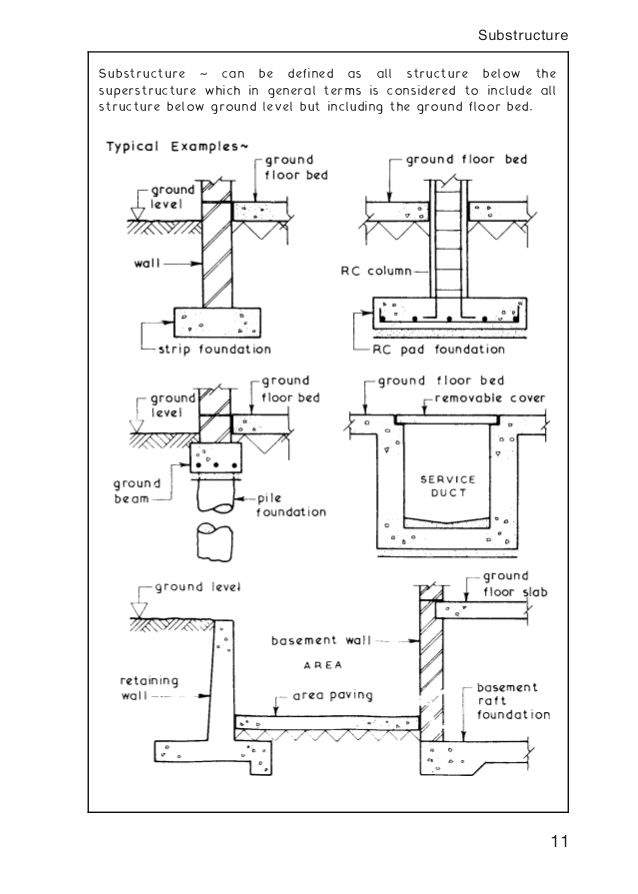
The substructure is the lower part of a building which is constructed below the ground level.
B4 4 earth retaining structures.
You can probably see the difference between the substructure and superstructure of buildings now but to make sure we have created a handy recap below.
So the substructure is in direct contact with supporting soil.
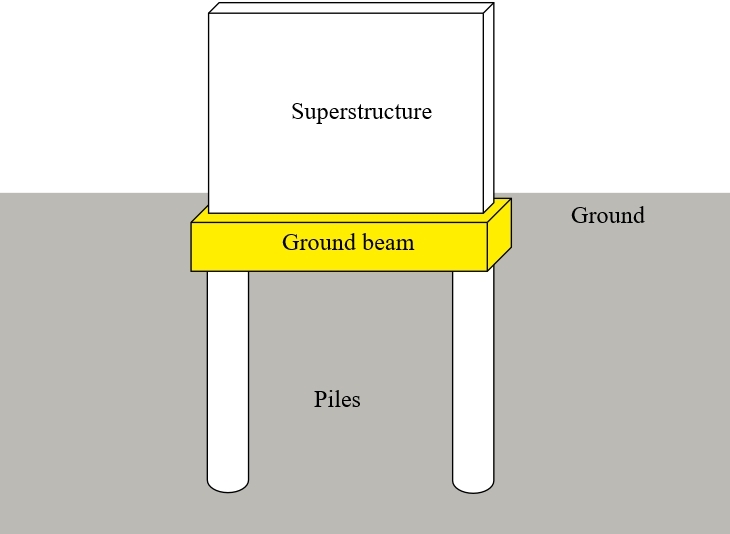
These components safely transfer the dead loads live loads and other loads to the substructure foundation and plinth which further distributes it to the underlying earth.
B4 6 superstructure principal loadbearing elements.
5 1 substructure and ground bearing floors.
Elements of a structure below the damp proof course dpc including the ground floor and foundations are known as the substructure.
The structure that is below the damp proof course that includes the ground floor and foundation.
B4 7 superstructure stability elements.
However substructure work is often one of the most challenging elements to measure.
B3 2 existing buildings appraisal.
B4 5 ground improvement.
Dampness from the ground and supporting structure should be prevented from reaching the floor by using linked dpms and dpcs to provide continuous protection.
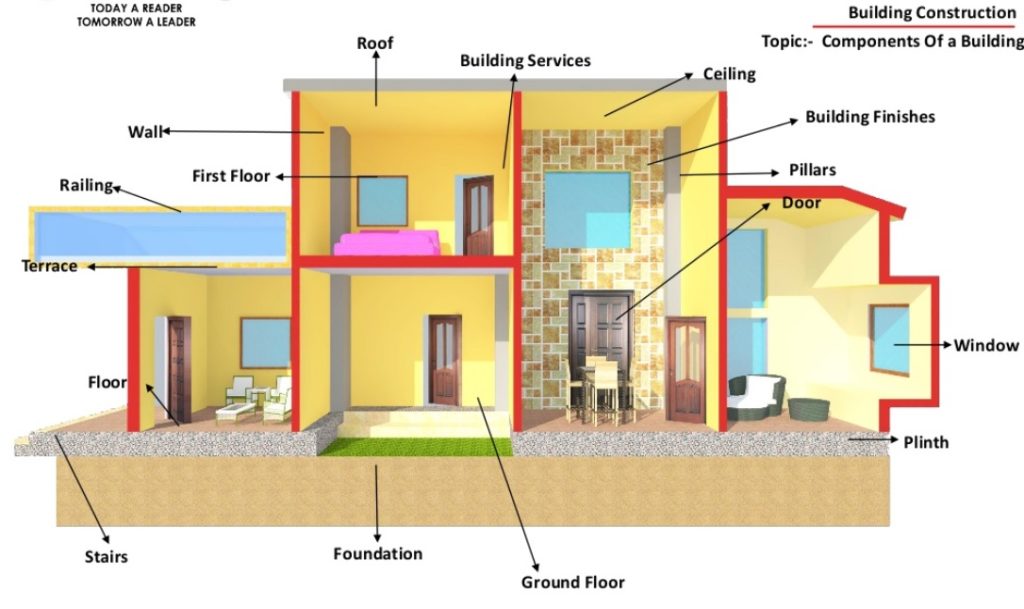
The basic components of a building s superstructure are columns beams slab and wall.
5 1 17 ground floor slab and concrete.
All the internal and external elements of a building above the substructure are referred to as the superstructure structure component below plinth up to.
B4 2 substructure including ground floor slab but excluding piling b4 3 piling.
B4 2 substructure including gound floor slab but excluding piling b4 3 piling.
Differences between the substructure and superstructure of a building.
B4 4 earth retaining structures.
5 1 18 laying the ground bearing floor slab.
The function of substructure is the transfer of loads from the superstructure to the underlying soil.
B4 8 superstructure other elements.
B4 9 structural ties fixings and connections.
B4 7 superstructure stability elements.
Substructure building superstructure building.
6 superstructure excluding roofs 6 1 external masonry walls.
Substructure involves footing and plinth of a building.
The structural components of a building constructed above the ground level constitute the superstructure.